
Baoyu ZHANG
Chinese Patent Attorney
In China, utility models and design patents adopt a preliminary examination system, making them less stable than invention patents. As a supplement to the preliminary examination system, China has established a patent right evaluation report system. This article mainly explains the relevant content of the design patent right evaluation report.
I. The Nature, Function, and Application Scenarios of the Patent Right Evaluation Report
The patent right evaluation report is issued by the National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA) upon request. It involves searching for relevant prior art or designs related to a utility model or a design patent and analyzing and evaluating whether the patent meets the grant conditions stipulated by the Patent Law and its implementing regulations.
The patent right evaluation report does not directly determine the validity of the patent right. It is typically used as evidence in the adjudication and handling of patent infringement disputes, mainly for courts or local patent offices to determine whether to suspend related procedures. The report is not an administrative decision, and the requester cannot initiate an administrative appeal or administrative litigation based on it.
In practice, e-commerce platforms' online complaints and intellectual property customs recordals often require a positive patent right evaluation report.
II. The requesting timing, the requesting party, the subject matter, the issuance time, and the costs of the patent right evaluation report
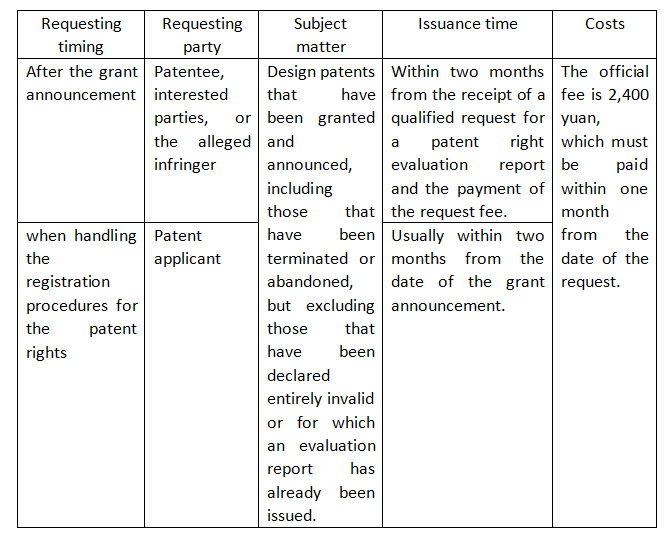
Interested parties refer to those who have the right, per Article 65 of the Patent Law, to initiate a lawsuit in the People's Court or request the relevant department in charge of patent affairs to handle a patent infringement dispute. For example, these include the exclusive licensee under a patent exclusive license agreement and the licensee under a patent ordinary license agreement who has been granted the right to sue by the patentee. Additionally, interested parties also include units or individuals who receive a legal letter from the patentee or a notice of complaint from an e-commerce platform, who are considered alleged infringers.
III. The procedures for requesting a patent right evaluation report
The request shall be submitted using the form prescribed by the CNIPA, specifying the application number or patent number, the title of the invention or creation, the name of the applicant or patent holder, and the name of the requester. If multiple requesters submit requests separately before the evaluation report is issued, the CNIPA will accept all requests but issue only one patent right evaluation report.
If the requester is a licensee under an exclusive patent license agreement, they shall submit the exclusive patent license agreement with the patent holder or a copy thereof. If the requester is a licensee under a non-exclusive patent license agreement authorized by the patent holder to initiate legal proceedings, they shall submit the non-exclusive patent license agreement with the patent holder or a copy thereof, along with proof of the patent holder's authorization to sue.
If the requester is an alleged infringer, they shall submit documents such as a notice of case filing issued by a people's court or a copy thereof, a notice of case filing issued by a patent administrative enforcement authority or a copy thereof, a case filing document issued by a mediation or arbitration institution or a copy thereof, a lawyer's letter issued by the patent holder or a copy thereof, or a complaint notice from an e-commerce platform or a copy thereof.
IV. Correction of the Patent Right Evaluation Report
The department issuing the patent right evaluation report may independently correct any errors found in the report.
If the requester believes there are errors in the patent right evaluation report that need correction, they may request a correction. Correctable content includes: errors in bibliographic information or text, procedural errors in issuing the patent right evaluation report, obvious errors in the application of law, obvious errors in the facts on which the conclusion is based, and other errors that should be corrected.
If the requester is not the patent holder, the patent holder may also submit a correction request.
V. Application Strategies of the Patent Holder or Interested Parties Regarding the Patent Right Evaluation Report
A positive evaluation conclusion can serve as evidence of patent validity. When competitors question the validity of a patent or when potential infringement occurs, the patent holder or interested parties can present the patent right evaluation report to demonstrate that the patent has undergone professional assessment, meets grant conditions, and possesses strong stability, thereby gaining an advantageous position in disputes. For partners, investors, licensees, and other relevant parties, a positive patent right evaluation report helps enhance their confidence in the patent’s value and market prospects.
To avoid receiving a negative evaluation conclusion, before requesting a patent right evaluation report, the patent holder or interested parties may engage professionals to conduct searches and stability assessments. For design patents regarded as relatively stable, an official evaluation report can be requested.
Even if the patent holder or interested parties receive a negative patent right evaluation report, there is no need for excessive concern. A negative evaluation report does not negate the validity of the patent, as patent validity is determined through invalidation proceedings. Therefore, for negative evaluation results, the reasons and evidence in the evaluation report should be carefully analyzed to assess their impact on the patent’s validity, and strategies for subsequent enforcement should be formulated or adjusted accordingly. If errors are found in the patent right evaluation report, a correction request should be submitted within two months of receiving the report to promptly rectify the erroneous evaluation.
VI. Application Strategies of the Alleged Infringer Regarding the Patent Right Evaluation Report
After receiving a legal letter from the patentee, a notice of complaint from an e-commerce platform, or a summons from the first-instance court or a notification from the department in charge of patent affairs, the alleged infringer should immediately verify whether a patent right evaluation report has been requested for the involved design patent. If no request has been made, the alleged infringer should promptly submit a request to the CNIPA.
If the conclusion of the evaluation report is that the patent meets the grant conditions, the alleged infringer may continue to search for strong evidence that could prove the invalidity of the design patent and may timely initiate an invalidation declaration procedure. If the conclusion is that the patent does not meet the grant conditions, the alleged infringer should apply to the court for a stay of proceedings and, based on the content of the evaluation report, try to add stronger evidence to initiate a patent invalidation declaration procedure.
If the alleged infringer believes that the patent right evaluation report contains errors, they should promptly request corrections, explaining the reasons to the CNIPA and providing relevant evidence to strive for a more accurate report result.
Open wechat "scan", open the page and click the share button in the upper right corner of the screen